Content
Winter is a wonderful time of the year. After the exhausting summer heat, many of us are looking forward to frost, snow, cleanliness. However, not everyone is given to fully enjoy the joys of winter. There are people who are forced to avoid frost, wind and any sudden changes in temperature, as they suffer from an allergy to cold.
Allergy to cold (cold allergy) is a type of allergic reaction, in which the effect of low temperatures acts as a provoking factor. Cold allergy is not an allergy in its purest form (pseudo-allergy), since there is no allergen. Previously, medicine did not even consider this type of allergy as a diagnosis. However, recent
You will learn about the causes of allergy to cold and methods of its treatment from this article. Studies show that about 30% of the population suffers from an increased reaction to cold to a greater or lesser extent, so this information is relevant.
. Moreover, women and children are more likely to be affected by this scourge, that is, those whose skin is thinner and more delicate.
Why does such a reaction occur and how to deal with it?
Causes
As with any allergic reaction, the symptoms of a cold allergy are caused by histamine. In this case, it is released by mastocytes - cells located very close to the skin . Why this happens precisely under the influence of cold has not yet been thoroughly studied. A number of factors have been identified that can provoke the onset of intolerance to low temperatures.
Provoking factors
Failure of the immune system can be caused by both external and internal causes, namely:
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- diseases of the endocrine system, liver, kidneys;
- oncological diseases;
- chronic ENT diseases;
- caries;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- genetic predisposition;
- asthma;
- eczema, psoriasis;
- the presence of any other allergic reactions.
Thus, it becomes clear that cold allergy often occurs against the background of depleted immunity and in the presence of other diseases.
Also at risk are people with congenital hypersensitivity of the skin, thin skin, young children.
Symptoms of the disease
The reaction to cold can have various external manifestations:
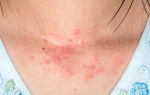
1. Cold urticaria . Manifestations of cold urticaria occur on areas of the skin that are in direct contact with a cold environment: hands and face. The skin turns red, blistered, rash, itchy, and sometimes burning.
2. Cold rhinitis . When going out into the cold, the patient's nose is blocked, the mucous surfaces swell, discharge (snot) is abundantly produced. As a rule, after returning to a warm room, these manifestations disappear within 30-60 minutes.
3. Cold conjunctivitis . Under the influence of cold, and especially in windy weather, the eyes turn red, watery, and begin to itch.
4. Cold asthma . When a patient inhales cold air, shortness of breath appears, breathing becomes difficult, bronchopulmonary spasm occurs, and an asthmatic attack develops. In severe cases, suffocation occurs.
5. Cold dermatitis . In the cold, the skin turns red, it hurts, a rash appears, dry skin, severe itching, burning. It is important not to comb the affected areas to avoid infection.
Also, the reaction to cold is often accompanied by headache, muscle pain, increased body temperature and blood pressure.
Obviously, the signs of a cold allergy are very similar not only to the symptoms of any other type of allergic reaction, but they can be easily confused with the onset of SARS.
Is it possible to self-diagnose the disease?
How not to be mistaken, what is it: an allergy to cold or SARS?
Runny nose, lacrimation, headache, pain in the joints and muscles can accompany both an incipient respiratory infection and a cold allergy. The difference is as follows:
- symptoms of allergy to cold gradually disappear within 30-60 minutes after returning to a warm room, while with ARVI the symptoms do not disappear, but only intensify with time;
- body temperature with ARVI often reaches 38-39℃, and with allergies it fluctuates in the range of 37-38℃;
- SARS does not have skin manifestations, such as: redness, itching, swelling, rash.
Also, if the patient has an identified allergy to any substance, and contact with the allergen is excluded, and characteristic symptoms appear when going out into the cold, the development of an allergic reaction to cold can be suspected.
Treatment
Obviously, the treatment of any intolerance is based on the prevention of contact with the allergen. The main difficulty is that it is impossible to do this at low temperatures. In the case when it is reliably established that an allergy to cold is a consequence of another disease, it is first necessary to eliminate the root cause (if possible). Otherwise, only the option of symptomatic treatment remains, corresponding to the type and intensity of allergy manifestations - the use of antihistamines , ointments, nasal drops and sprays, special eye drops.
Prevention
The following techniques are designed to reduce or completely prevent an allergic reaction:
- 20-30 minutes before going outside, you can lubricate the skin with badger fat or any greasy cream. The cream will create a protective film, prevent chapping, strengthen the barrier functions of the skin. Important: the cream should not be moisturizing. The water contained in the moisturizer will turn into ice crystals in the cold, which will additionally injure skin cells, only aggravating the symptoms;
- be sure to use oily hygienic lipstick;
- additionally protect exposed areas of the skin: put warm mittens on your hands, wrap your nose and cheeks with a scarf, hide from gusts of wind by wearing a hood;
- wear clothes made from natural hygroscopic fabrics - synthetics and wool can provoke an allergic reaction;
- for cold rhinitis, use antihistamine nasal sprays before going outside;
- take multivitamin complexes, as well as eat foods rich in fats and amino acids: nuts, oily fish, vegetable oils;
- give up decorative cosmetics and perfumes - they can also provoke an immune reaction.
In addition, an allergy to cold can be corrected by hardening.
hardening
Hardening strengthens small vessels and intercellular connections, which allows you to train the body to overcome sudden temperature changes and reduce the manifestations of an allergic reaction in the future.
It is better to start hardening with rubbing with a towel soaked in cold water (about 18℃), gradually increasing the procedure time. Then you can move on to pouring. The water should not be immediately cold: every week the water temperature is lowered by 1℃, starting from 36-37℃. If allergy symptoms appear at some stage of hardening, the temperature should be raised by 1℃ and not lowered for another 1-2 weeks. The main principles in hardening are regularity and gradualness.
Allergy to cold is a very unpleasant disease, and it can and should be treated. Regardless of the severity of allergic manifestations, it is necessary to visit an allergist. He will help to find the true cause of the disease (and it may turn out to be a much more serious disease) and select the most appropriate therapy.